How To Recover From A Stroke
Well-managed stroke rehabilitation is key to reducing the time it takes to recover from a stroke. A stroke occurs when an artery in the brain becomes damaged, impeding the flow of oxygen to the brain. If or when a stroke happens it’s important to get immediate medical treatment, followed by rehabilitation. This will improve your chances of a swifter recovery.
Strokes can happen to people of any age but are more common in the elderly. How long it takes to recover from a stroke will depend on many factors including the patient’s overall medical condition.
Another key factor is the severity of the stroke and exactly which part of the brain it affected. While some stroke survivors recover quickly, most need some form of longer-term stroke rehabilitation, lasting possibly months or sometimes even years.
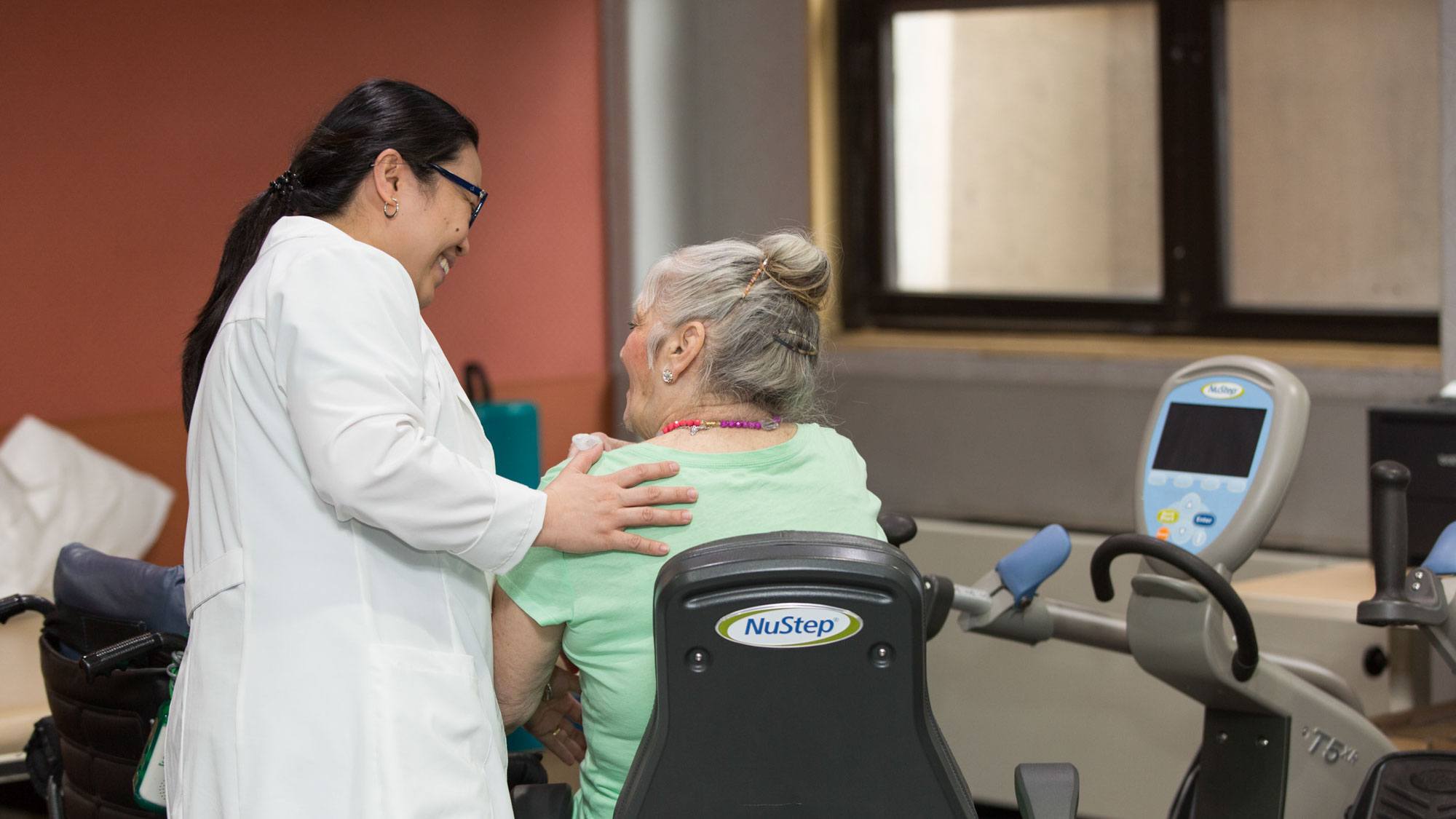

Good care for speedy recovery from a stroke
Since strokes usually affect a person’s mobility, quality care and rehabilitation therapies by trained professionals with experience of treating strokes is essential.
It’s important that rehabilitation starts quickly to take advantage of the brain’s heightened repair work activity at this time. The fastest period of recovery usually takes place in the first two weeks after a stroke.
The initial aim of rehab is to stabilize the patient and prevent complications such as pressure ulcers and muscle atrophy. Later, rehab will include administration of the right medication and a variety of therapies to aid recovery from a stroke. These could be physical, occupational and speech therapy.
Many stroke sufferers lose full control of their ability to swallow normally. However, specific exercises can strengthen your control over swallowing and eating.
Good care in the longer run also implies loving care, social interaction and the emotional support of friends and family.
Physical therapy
The aim of rehab is to help you regain as much mobility and independence as possible. Each person’s ability to recover quickly will vary but physical therapy supervised by skilled practitioners is key. In addition, physical therapists will focus on getting the limb or limbs which don’t work to work better.
Your rehab plan will be tailored to the severity of your stroke and your overall health condition. Physical therapy includes exercises to help improve your muscle strength and coordination. There are also therapies designed to ease muscle tension and thus improve your range of motion.
Occupational therapy
Another essential tool on the road to recovery from a stroke is occupational therapy. This can help you regain lost cognitive abilities, social skills and safety awareness. The occupational therapist helps patients improve their sensory and motor abilities and master the essential tasks of daily living. These include dressing, eating, bathing and writing. Occupational therapy can also help you continue to do things you might enjoy doing like, knitting, painting or playing cards.
In addition, therapists can help you relearn how to walk and keep your balance, perhaps using a cane or walker. They can also help you practice using other mobility aids such as a wheelchair or ankle brace.
Occupational therapy is designed to improve the quality of your life after a stroke. So, occupational therapists give survivors practical tips on how to adapt to their new situation. They can also teach patients how to divide a complex activity into smaller parts. Together they then practice each part until the patient can perform the entire sequence of the activity.
Fairview rehab & nursing home
After a stroke you and your family will need to decide on the best rehab setting. Rehab can take place in inpatient rehabilitation units, outpatient units, skilled nursing facilities or at home. Fairview Rehab and Nursing Home in Queens, NY, has lots of experience helping stroke patients to recover. The facility provides both in- and outpatient physical, occupational, speech therapies, taking advantage of all the latest technologies. Our friendly, multilingual staff are always on hand to speed your recovery from a stroke.
This article contains informational and educational materials and does not replace health or medical advice. For questions or concerns regarding your medical condition or health objectives, speak to a qualified physician or healthcare provider.




Leave A Comment