Orthopedic Rehabilitation: When Do You Need It
The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage and is more delicate than most people realize. As well as forming our body’s structure, it dictates posture and movement. When any area is damaged, specialized orthopedic rehabilitation is required to ensure proper healing.
Musculoskeletal rehab consists of various facets of physical therapy, which are customizable to match your diagnosis. It benefits those after injury or surgery, offering prolonged healing of bones and other tissue. It also reduces pain and increases mobility while managing any chronic conditions that cause issues or slow recovery.
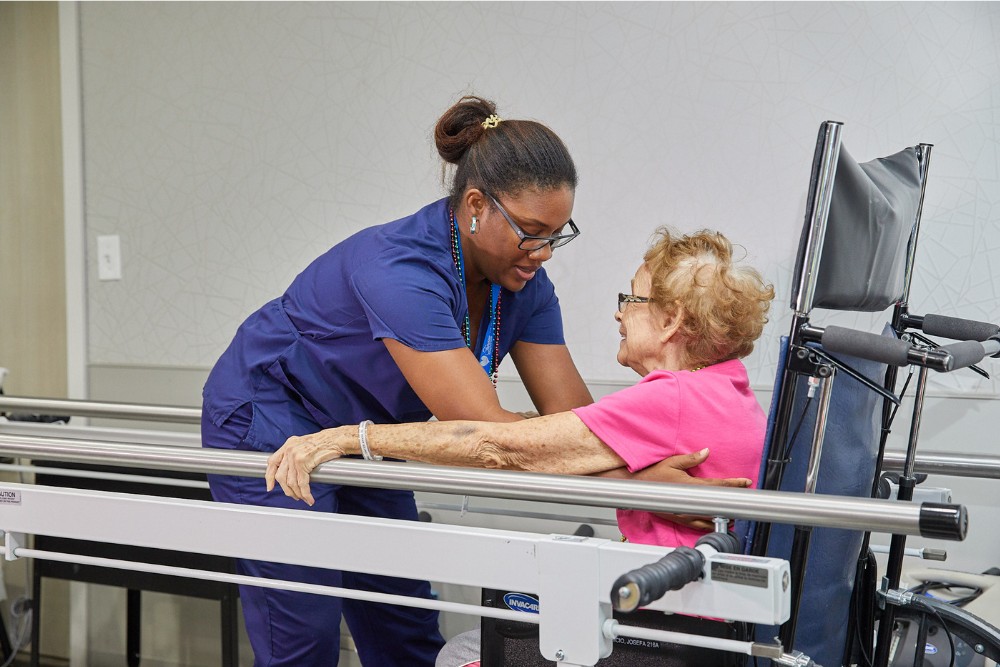

Orthopedic rehabilitation is crucial when recovering from injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, such as fractures, joint replacements, or arthritis. It helps restore strength, mobility, and function to areas like the bones, joints, muscles, and tendons. If you’re experiencing persistent pain, limited range of motion, or difficulty performing daily activities, rehabilitation guided by physical or occupational therapists can aid recovery. It’s also important after orthopedic surgeries to ensure proper healing, prevent complications, and regain full functionality. Early rehabilitation can speed up recovery and improve long-term outcomes.
Speed Up Bone Repair with Orthopedic Rehabilitation
Adult skeletons consist of 206 bones, which give us our shape, keep us upright, and protect our vital organs. Though they have various shapes, sizes, types, and functions, each bone is a critical piece of the human puzzle.
When bones are fractured, they go through an intricate healing process involving several stages and processes. When healing slows or halts, it causes several possible problems, including infection, delayed or non-union, tumors, or misalignment.
Orthopedic rehabilitation features treatments designed to improve bone repair for a faster recovery. Assistive devices, therapeutic stimulation, and patient education ensure the bones heal correctly in minimal time.
Chronic conditions
Several chronic conditions affect the bones, joints, and other areas of the musculoskeletal system. These include osteoporosis, fibromyalgia, scoliosis, osteonecrosis, and arthritis. Bones also may wear out over time, most commonly the knees and hips.
Though some issues are curable, many require ongoing treatment to manage the symptoms and slow the progression. After a thorough evaluation and diagnosis, orthopedic rehabilitation offers tailored treatments for your issues.
These include passive or active therapy, exercise programs, hot and cold therapy, and movement retraining. Trained professionals work with you to determine the best course of action for your condition, goals, and limitations.
Limited mobility and pain
Injuries, trauma, or surgical intervention to repair damage often cause similar problems, including mobility limitations and pain. Sometimes these issues are long-lasting, especially if affecting the bones and joints needed for most movements.
The treatments included in orthopedic rehabilitation are designed to restore your former physical abilities. Physical therapy programs include exercises that help you rebuild strength, endurance, flexibility, and balance to improve mobility.
These customizable sessions include pain management methods, such as cold or heat therapy and dry needling. Experts believe electrical stimulation, including transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), is also effective for treating musculoskeletal pain.
Prolonged healing
Minor injuries usually don’t take long to heal, so you’re back to your old self in no time. More serious trauma, especially issues requiring surgery, often requires months or even years for a full recovery.
Prolonged healing is also delicate since your physical functions aren’t the only ones at risk. Slow recoveries often take a toll on your psychological functions as well, resulting in depression, anxiety, and stress.
The techniques used in orthopedic rehabilitation often shorten hospital stays, reduce complications, and improve functions. As you meet or exceed your recovery goals, negative thoughts decrease, and you regain your positive outlook. The better you feel about your progress, the more motivated you’ll be to continue therapy.
Orthopedic rehabilitation helps with prolonged healing by providing targeted exercises and therapies that gradually rebuild strength, flexibility, and mobility in injured or surgically repaired areas. It encourages proper alignment and movement patterns, which reduces the risk of re-injury and promotes faster recovery. Rehabilitation also improves blood circulation, which enhances tissue repair and reduces swelling. By addressing muscle imbalances and stiffness, it prevents complications like joint stiffness or muscle atrophy that can occur during extended healing periods. Regular sessions also offer pain management techniques, allowing for a more comfortable recovery process.
Resources:
- Healthdirect, Bones, muscles, and joints
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bones-muscles-and-joints#:~:text=Bones%2C%20muscles%20and%20joints%20make%20up%20the%20musculoskeletal%20system%2C%20along,damage%20bones%2C%20muscles%20and%20joints. - NCBI, April 8, 2023, Fracture Healing Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551678/ - NIAMS, Muscle and Bone Diseases
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/muscle-bone-diseases - USC Physical Therapy, Orthopedic Rehabilitation
https://pt.usc.edu/patient-care/orthopedic-rehabilitation/ - IASP, January 26, 2023, Using TENS for Pain Control: Update on the State of the Evidence
- NCBI, February 26, 2023, Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Rehabilitation Protocol in the Perioperative Period of Orthopedics: A Systematic Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10052010/
This article contains informational and educational materials and does not replace health or medical advice. For questions or concerns regarding your medical condition or health objectives, speak to a qualified physician or healthcare provider.





Leave A Comment